|
| Method no.: |
PV2102 |
| |
|
| Control no.: |
T-PV2102-01-8709-CH |
| |
|
| Matrix: |
Air |
| |
|
| Target Concentration: |
5 mg/m3 (arbitrary).
There is no OSHA PEL or ACGIH TLV for Apron. |
| |
|
| Procedure: |
Samples are collected by drawing
60 L of air through glass fiber filters. Samples are extracted
with acetonitrile and analyzed by high performance liquid
chromatography (HPLC). |
| |
|
| Recommended air volume and
sampling rate studied: |
60 L at 1 L/min |
| |
|
| Detection limit of the overall
procedure based on the recommended air volume: |
0.02 mg/m3 |
| |
|
| Status of method: |
Stopgap method. This method has
been only partially evaluated and is presented for information
and trial use. |
| |
|
| Date: |
September 1987 |
| |
|
| Chemist: |
Yihlin Chan |
| |
|
Carcinogen and Pesticide Branch
OSHA Analytical
Laboratory
Sandy, Utah
|
1. General discussion
1.1
Background
The OSHA
Analytical Laboratory received a set of samples for
which an analysis of Apron was requested. The air
samples had been collected on glass fiber filters at a flow
rate of 1 L/min. This report describes the analytical method
developed for Apron and a preliminary validation of glass
fiber filter as the sampling medium.
1.2 Toxic
effects (This section is for information only and should not
be taken as the basis of OSHA policy.)
The oral
LD50 of Apron is 669 mg/kg in rats. The acute
dermal LD50 is >3100 mg/kg for rats. It is
relatively non-toxic to fish and wildlife. (Ref.
5.1)
1.3 Potential workplace exposure (Ref.
5.3)
Apron is used as a fungicide in
agricultural applications. No estimate of worker exposure
during its production, formulation and use as a fungicide
could be found.
1.4 Physical properties (Ref.
5.1 and 5.2)
| Chemical name: |
N-(2,6-Dimethylphenyl)-N-(methoxyacetyl)
-DL-alanine methyl ester |
| Synonym: |
Apron 2E; CG
117; CGA 48988; Metalaxil; Ridomil; Ridomil 2E;
Subdue; Subdue 2E; Subdue 5SP;
N-(Methoxyacetyl)-N-(2,6-xylyl)-DL-alanine methyl
ester |
| CAS no.: |
57837-19-1 |
| Molecular
formula: |
C15H21NO4 |
| Molecular
weight: |
279.37 |
| Appearance: |
White
crystals |
| Melting
point: |
71-72°C |
| Vapor
pressure: |
2.2×10-6
mmHg at 20°C |
Structure:

| Solubility: |
Solubility in
water at 20°C: 7.1 g/L. Readily soluble in most
organic solvents. |
| UV
scan: |
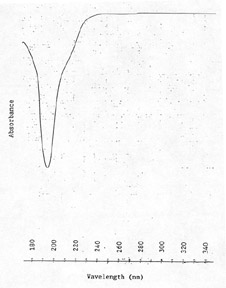 | 1.5
Detection limit of the analytical
procedure
The detection
limit of the analytical procedure is 4.3 ng
per injection. 2. Sampling procedure
2.1 Apparatus and
reagents
2.1.1 A personal sampling
pump that can be calibrated to within 5% of the
recommended flow rate.
2.1.2 Glass fiber
filter, 37-mm diameter, Gelman Type A, or
equivalent.
2.1.3 Filter holder for 37-mm
filters, Millipore M000037A0, or equivalent.
2.2 Sampling
procedure
Use
standard air sampling technique as specified in OSHA
Instruction CPL 2-2.20A, Chapter II: Standard Methods for
Sampling Air Contaminants.
2.3 Recommended air volume and sampling
rate
2.3.1 The recommended
air volume is 60 L.
2.3.2 The recommended
sampling rate is 1 L/min.
2.4 Extraction efficiency
Three glass fiber filters were each spiked
with 16.35 µg of Apron. The filters were extracted with
5.0 mL of acetonitrile and analyzed. The average recovery of
Apron was 100.4%.
|
Sample |
Apron recovered |
Recovery |
|
| YC1 |
16.07 µg |
98.3% |
| YC2 |
16.60 µg |
101.5% |
| YC3 |
16.56 µg |
101.3% |
|
Average |
=
100.4% |
|
2.5
Retention efficiency
Three
glass fiber filters were each spiked with 16.35 µg of Apron.
Humid air (50% RH, 183 L @ 1 L/min) was drawn through the
filters. The filters were extracted with 5.0 mL of
acetonitrile and analyzed. The average recovery of Apron was
97.9%.
| Sample |
Apron
recovered |
Recovery |
|
| YC7 |
15.46 µg |
94.6% |
| YC8 |
16.40 µg |
100.3% |
| YC9 |
16.13 µg |
98.7% |
|
Average |
= 97.9% |
| 2.5
Storage
Three glass fiber
filters were each spiked with 16.35 µg of Apron. Humid air
(50% RH, 183 min @ 1 L/min) was drawn through the filters.
The filters were stored at room temperature for 5 days,
extracted with acetonitrile, and analyzed. The average
recovery of Apron was 104.9%.
| Sample |
Apron
recovered |
Recovery |
|
| YC10 |
17.05 µg |
104.3% |
| YC11 |
17.05 µg |
104.3% |
| YC12 |
17.33 µg |
106.0% |
|
Average |
=
104.9% |
| 2.6
Interferences
There
are no known interferences to the sampling procedure.
3. Analytical
method
3.1 Apparatus
3.1.1 High performance
liquid chromatograph.
3.1.2 Alltech
C18 column or equivalent.
3.1.3 UV
detector.
3.1.4 Stripchart recorder.
3.2 Reagents
3.2.1 Water, HPLC
grade.
3.2.2 Acetonitrile, HPLC
grade.
3.2.3 Apron (Ridomil), EPA standard #
F701. 3.3
Standard preparation
Weigh
2 to 4 mg of Apron in a 10-mL volumetric flask.
Add acetonitrile to the mark. Dilute with acetonitrile
to a suitable working range.
3.4 Sample preparation
Samples were extracted with 5.0 mL of
acetonitrile, 30 minutes on a mechanical
shaker.
3.5
Analysis
3.5.1 Instrument
conditions
| Column: |
Alltech
C18 |
| Mobile
phase: |
60%
acetonitrile, 40% water |
| Detector: |
198 nm
(primary), 214 nm |
| Flow
rate: |
1.0
mL/min |
| Injection
size: |
25
µL |
| Retention
time: |
7.0
min | 3.5.2 Chromatogram
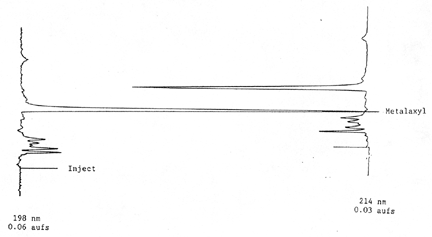
Figure 1.
HPLC Chromatogram of Apron.
3.6 Interferences
3.6.1 Any collected
compound that has the same retention time as Apron and
absorbs at 198 and 214 nm is an
interference.
3.6.2 HPLC parameters may be
varied to circumvent most
interferences.
3.6.3 Retention time alone is
not proof of a chemical identity. Confirmation by other
means should be sought when possible.
3.7 Calculations
3.7.1 A calibration curve
is constructed by plotting standard concentrations versus
detector response.
3.7.2 The concentration of
a sample is determined from the calibration
curve.
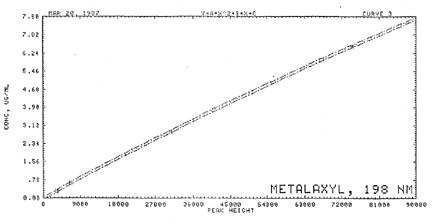
Figure
2. Calibration curve of
Apron.
3.7.3 The
air concentration is determined by the
formula:
| mg/m3 = |
(µg/mL)(5
mL) |
|
| (air
volume, L)(extraction
efficiency) | 4. Recommendations for further
study
The method should be
fully validated.
5. References
5.1 Registry of Toxic
Effects of Chemical Substances, 1983-84 Supplement,
DHHS (NIOSH) Publication No. 86-103, Cincinnati, Ohio,
1986.
5.2 Merck Index, Tenth Edition, Merck
& Co., Rahway, N.J., 1983.
5.3 Farm
Chemicals Handbook, Meister Publishing, Willoughby, Ohio,
1981.
|
| |
| |

