Butyl carbitol |
| Method no.: | PV2095 |
| Control no.: | T-PV2095-01-9302-CH |
| Matrix: | Air |
| Target concentration: | 25 ppm (166 mg/m3) butyl carbitol 25 ppm (205 mg/m3) butyl carbitol acetate |
| Procedure: | Samples are collected by drawing a known -volume of air through a charcoal tube. Samples are desorbed with 5:95 methanol:methylene chloride and analyzed by gas chromatography with a flame ionization detector (GC-FID). |
| Air volume and sampling rate studied: | 10 liters at 0.2 Lpm. |
| Status of method: | Stopgap method. This method has been only partially evaluated and is presented for information and trial use. |
| Date: | February, 1993 |
| Chemist: | Mary E. Eide |
Organic Service Branch
I
OSHA Technical Center
Salt Lake City, Utah
1. General Discussion
1.1 Background
1.1.1 History of procedure
There have been many requests for sampling and analytical procedures for butyl carbitol and butyl carbitol acetate. They have been directed to follow OSHA method 83 for 2-butoxyethanol, since butyl carbitol is related to this compound (Ref. 5.1). This study was undertaken to gather the data necessary to verify that this is the proper procedure. In method 83, collection of 2-butoxyethanol is on charcoal tubes. Desorption of butyl carbitol from charcoal tubes was previously attempted using carbon disulfide, but the recovery was 71%, while butyl carbitol acetate had a 83.4% recovery. These recovories were low and a better desorbing solvent was needed. A solution of 5:95 methanol:methylene chloride is used in OSHA method 83 to desorb 2-butoxyethanol from charcoal. This solvent was tried and found to give desorptions of 99.2% for butyl carbitol and 10OX for butyl carbitol acetate. Retention and storage studies showed good recoveries for charcoal tubes.
1.1.2 Potential workplace exposure (Ref. 5.2)
Butyl carbitol and butyl carbitol acetate are used as a solvent for nitrocellulose, oils, dyes, gums, soaps, and polymers, and as a pasticizer in lacquers and coatings.
1.1.3 Toxic Effects (This section is for information purposes and should not be taken as the basis for OSHA policy.)(Ref. 5.3)
Butyl carbitol and butyl carbitol acetate are skin, eye, and mucous membrane irritants. In rabbits, 5 mg butyl carbitol applied to the eye resulted in severe irritation. For butyl
carbitol, the LD50 orally in guinea pigs is 2000 mg/kg, and through the skin in rabbits is 4120 mg/kg. For butyl carbitol acetate, the LD5O orally in guinea pigs was 2340 mg/kg, and through the skin in rabbits was 14500 mg/kg. The eye irritation in rabbits of butyl carbitol acetate was mild for a 500 mg exposure.1.1.4 Physical properties (Ref. 5.2):
Butyl carbitol
Compound: Synonyms: 2-(2-butoxyethoxy)ethanol; diethylene glycol monobiityl ether; butyl digol; but,rl diicinol; butoxydiethylene glycol; butoxydiglycol; butyl dioxitol; Dowanol DB; Ektasolve DB; glycol ether DB; jeffersol DB; poly-solv DB
Molecular weight: 162.22 Density: 0.9536 Boiling point: 230.4°C Freezing point: -68°C Flash point: 78°C (172°F)(closed cup) Autoignition
temperature:228°C (442°F) Odor: odorless Color: clear liquid Molecular formula: C8H18O3 CAS: 112-34-5 IMIS: 0471 RTECS: 34278 (KJ9100000) Butyl carbitol acetate
Compound: Synonyms: 2-(2-Butoxyethoxy)ethanol acetate; Diethylene glycol butyl ether acetate; 2-(2-Butoxyethoxy)ethyl acetate; Diethylene glycol monobutyl ether acetate; Diglycol monobutyl ether acetate; Ektasolve DB acetate; Glycol ether DB acetate Molecular weight: 204.30 Density: 0.981 Boiling point: 247°C Freezing point: -32°C Flash point: 115°C (240°F)(open cup) Autoignition
temperature:299°C (570°F) Odor: odorless Color: clear liquid Molecular formula: C10H20O4 CAS: 124-17-4 IMIS: M316 RTECS: 34278 (KJ9100000) 1.2 Limit defining parameters
1.2.1 The detection limit of the analytical procedure is 5 ng butyl carbitol and butyl carbitol acetate, with a 1 µL injection volume. This is a 5 pg/mL analytical standard. This is the smallest amount which could be detected under normal operating conditions.
1.2.2 The overall detection limit is 0.08 ppm butyl carbitol and 0.06 ppm butyl carbitol acetate based on a 10 liter air volume. (All ppm amounts in this study are based on a 10 L air volume.)1.3 Advantages
1.3.1 The sampling procedure is convenient.
1.3.2 The analytical method is reproducible and sensitive.
1.3.3 Re-analysis of samples is possible.
1.3.4 It may be possible to analyze other compounds at
the same time.1.3.5 Interferences may be avoided by proper selection of column parameters.
1.4 Disadvantages
Methylene chloride is very volatile. A fan blowing on the instrument may be advisable to obtain replicate injections, when using an autosampler.
2. Sampling procedure
2.1 Apparatus
2.1.1 A calibrated personal sampling pump, the flow of
which can be determined within ±5% at the recommended flow.2.1.2 Charcoal tubes, lot 120, containing 100 mg adsorbing section with a 50 mg backup section separated by a 2 mm portion of urethane foam, with a silane treated glass wool plug before the adsorbing section and a 3-mm plug of urethane foam at the back of the backup section. The ends are flame sealed and the glass tube containing the adsorbent is 7 cm long, with a 6-mm O.D. and 4-mm I.D., SKC tubes or equivalent.
2.2 Sampling technique
2.2.1 The ends of the charcoal tube are opened immediately before sampling.
2.2.2 Connect the charcoal tube to the sampling pump with flexible tubing.
2.2.3 Tubes should be placed in a vertical position to minimize channeling, with the smaller section towards the pump.
2.2.4 Air being sampled should not pass through any hose or tubing before entering the charcoal tube.
2.2.5 Seal the charcoal tube with plastic caps immediately after sampling. Seal each sample lengthwise with OSHA Form-21 sealing tape.2.2.6 With each batch of samples, submit at least one blank tube from the same lot used for samples. This tube should be subjected to exactly the same handling as the samples (break ends, seal, & transport) except that no air is drawn through it.
2.2.7 Transport the samples (and corresponding paperwork) to the lab for analysis.
2.2.8 Bulks submitted for analysis must be shipped in a separate mailing container from other samples.
2.3 Desorption efficiency
Six tubes were spiked with 0.167 mg (2.52 ppm), O.E34 mg (12.6 ppm), 1.67 mg (25.2 ppm), and 3.34 mg (50.3 ppm) butyl carbitol, and 0.206 mg (2.47 ppm), 1.03 mg (12.3 ppm), 2.06 mg (24.7 ppm), and 4.12 mg (49.3 ppm) butyl carbitol acetate. They were allowed to equilibrate overnight at room temperature. They were opened, each section placed into a separate 2 mL vial, desorbed with 1 mL of the desorbing solution for 30 minutes with occasional shaking, and analyzed by gas chromatography with a flame ionization detector. The overall average for butyl carbitol was 99.2%. (Table 2.3.1) The overall average for butyl carbitol acetate was 100%. (Table 2.3.2)
Table 2.3.1 Butyl Carbitol Desorption Efficiency
Tube # % Recovered 0.167mg 0.834mg 1.67mg 3.34mg
1 99.3 97.4 99.9 98.9 2 97.9 98.1 101 100 3 97.8 98.8 102 99.4 4 98.5 97.7 101 99.6 5 97.6 98.9 101 99.9 6 96.7 97.5 99.7 101 average 98.0 98.1 101 99.8 overall average 99.2 standard deviation ±1.41
Table 2.3.2 Butyl Carbitol Acetate Desorption Study
Tube # % Recovered 0.206mg 1.03mg 2.06mg 4.12mg
1 99.2 103 99.9 99.8 2 100 101 99.5 100 3 100 100 99.8 101 4 99.7 99.8 101 100 5 101 100 100 101 6 99.4 99.2 99.3 100 Average 99.9 101 99.9 100 Overall average 100 Standard Deviation ±0.85
2.4 Retention efficiency
Six tubes were spiked with 3.34 mg (50.3 ppm) butyl carbitol and 4.12 mg (49.3 ppm) butyl carbitol acetate, allowed to equilibrate overnight, and had 10 liters humid air (90% RH) pulled through them at 0.2 Lpm. They were analyzed by GC-FID immediately. There was no butyl carbitol or butyl carbitol acetate found on the backup portions of the tubes. The retention efficiency averaged 99.3% for butyl carbitol and 99.4% for butyl carbitol acetate.(Table 2.4) Recoveries are desorption corrected.
Table 2.4 Retention Efficiency
% Recovered Tube Butyl Carbitol Butyl carbitol acetate # 'A' 'B' Total 'A' 'B' Total
1 97.3 0.0 97.3 99.9 0.0 99.9 2 98.7 0.0 98.7 98.2 0.0 98.2 3 101 0.0 101 99.7 0.0 99.7 4 98.5 0.0 98.5 100 0.0 100 5 101 0.0 101 99.1 0.0 99.1 6 99.1 0.0 99.1 99.5 0.0 99.5 average 99.3 average 99.4
2.5 Storage
Tubes were spiked with 1.67 mg (25.2 ppm) butyl carbitol and 2.06 mg (24.7 ppm) butyl carbitol acetate, and stored at room temperature until opened and analyzed. The recoveries averaged 98.8% for butyl carbitol and 98.7% for butyl carbitol acetate over the 14 days stored. Recoveries are desorption corrected. (Table 2.5)
Table 2.5 Storage Study
Day % Recovered Butyl carbitol Butyl carbitol acetate
7 96.8 101 7 98.4 97.5 7 98.3 101 14 102 97.4 14 99.6 97 14 97.7 98.2 average 98.8 98.7
2.6 Precision
The precision was calculated using the area counts from six injections of each standard at concentrations of 0.167, 0.834, 1.67, and 3.34 mg/mL butyl carbitol, and 0.206, 1.03, 2.06, and 4.12 mg/mL butyl carbitol acetate in the desorbing solution. The pooled coefficient of variation was 0.00392 for butyl carbitol and 0.00155 for butyl carbitol acetate. (Tables 2.6.1 and 2.6.2)
Table 2.61 Butyl Carbitol Precision Study
Injection Number 0.167mg/mL 0.834mg/mL 1.67mg/mL 3.34mg/mL
1 68887 153640 326647 634611 2 68884 152347 326851 634061 3 69226 154281 323728 635744 4 69149 152240 327083 639198 5 68920 153501 324953 637233 6 69105 152466 326786 637233 Average 69029 153079 326008 636367 Standard Deviation ±150 ±842 ±1356 ±1924 CV 0.00217 0.0055 0.00416 0.00302 Pooled CV 0.00392
Table 2.6.2 Butyl Carbitol Acetate Precision Study
Injection Number 0.206mg/mL 1.03mg/mL 2.06mg/mL 4.12mg/mL
1 66260 258265 518901 1037664 2 66352 258402 518456 1036916 3 66152 258504 517160 1038185 4 66521 257457 518661 1036115 5 66174 258713 517187 1039708 6 66527 257765 518581 1039627 Average 66331 258184 518158 1038036 Standard Deviation ±165 ±478 ±776 ±1444 CV 0.00249 0.00185 0.00150 0.00139 Pooled CV 0.00155
where:

A(1), A(2), A(3), A(4) = # of Injections at each level
CV1, CV2, CV3, CV4 = Coefficients at each level
2.7 Air volume and sampling rate studied2.7.1 The air volume studied is 10 liters.
2.7.2 The sampling rate studied is 0.2 liters per minute.
2.8 Interferences
Suspected interferences should be listed on sample data
sheets.2.9 Safety precautions
2.9.1 Sampling equipment should be placed on an
employee in a manner that does not interfere with work performance or safety.2.9.2 Safety glasses should be worn at all times.
2.9.3 Follow all safety practices that apply to the workplace being sampled.
3. Analytical method
3.1 Apparatus
3.1.1 Gas chromatograph equipped with a flame ionization detector. A Hewlett Packard 5890 gas chromatograph was used in this study.
3.1.2 An electronic integrator or some other suitable method of measuring peak areas.
3.1.3 GC column capable of separating the analyte and
an internal standard from any interferences. The column used in this study was a 15-meter DB-WAX capillary column, 0.32 mm I.D. with a 0.25 µm film thickness. An alternate column is a 60-meter DB-WAX capillary column, 0.32 mm I.D. with a 1.0 µm film thickness.3.1.4 Two milliliter vials with Teflon-lined caps.
3.1.5 A 10 µL syringe or other convenient size for a sample injection.
3.1.6 Pipets for dispensing the desorbing solution. The Glenco 1 mL dispenser was used in this method.
3.1.7 Volumetric flasks - 5 mL and other convenient sizes for preparing standards.
3.2 Reagents
3.2.1 Purified GC grade nitrogen, hydrogen, and air.
3.2.2 Butyl carbitol, Reagent grade
3.2.3 Butyl carbitol acetate, Reagent grade
3.2.4 Methanol, HPLC grade
3.2.5 Methylene chloride, HPLC grade
3.2.6 n-Hexanol, Reagent grade, used as an internal
standard3.2.7 The desorbing solution is 5:95 methanol:methylene chloride with 0.25 PL/mL n-hexanol internal standard.
3.3 Sample preparation
3.3.1 Sample tubes are opened and the front and back section of each tube are placed in separate 2 mL vials.
3.3.2 Each section is desorbed with 1 mL of the desorbing solution.
3.3.3 The vials are sealed immediately and allowed to desorb for 30 minutes with occasional shaking.
3.4 Standard preparation
3.4.1 Standards are prepared by diluting a known
quantity of butyl carbitol and butyl carbitol acetate with the desorbing solution.3.4.2 At least two separate standards should be made.
3.4.3 A third analytical standard should be prepared at a higher concentration to check the linearity of the detection. For this study two standards at 1 µL/mL (0.954 mg/mL butyl carbitol and 0.981 mg/mL butyl carbitol acetate) and one standard at 4 µL/mL (3.82 mg/mL butyl carbitol and 3.92 mg/mL butyl carbitol acetate) were used.
3.5 Analysis
3.5.1 Gas chromatograph conditions for 15-meter DB-WAX capillary column.
Flow rates (mL/min.)
Temperature (°C)
Nitrogen(make-up): 30 Injector: 180 Hydrogen(carrier): 2 Detector: 220 Hydrogen(detector): 30 Column: 60°C for 2 min Air: 350 10°C/min to 130°C Injection size: 1 µL Chromatogram:
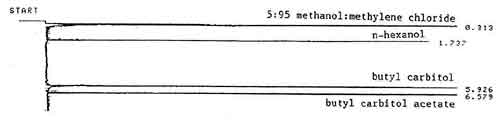
Figure 1. An analytical standard of 1 µL/mL butyl carbitol and butyl carbitol acetate in the desorbing solvent of 5:95
methanol:methylene chloride with 0.25 µL/mL n-hexanol
internal standard, analyzed on a 15-meter DB-WAX capillary column.3.5.2 Gas chromatograph conditions for 60-meter DB-WAX capillary column.
Flow rates (mL/min.) Temperature (°C) Nitrogen(make-up): 30 Injector: 180 Hydrogen(carrier): 2 Detector: 220 Hydrogen(detector): 30 Column: 100 °C for 2 min 10°C/min to 180°C Air:
350 Injection size: 1 µL Chromatogram:
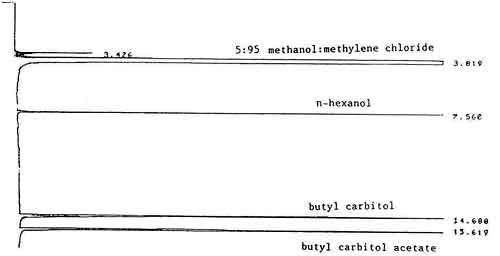
Figure 2. An analytical standard of 1 µL/mL butyl carbitol and butyl carbitol acetate in the desorbing solvent of 5:95
methanol:methylene chloride with 0.25 µL/mL n-hexanol
internal standard, analyzed on a 60-meter DB-wax column.3.5.3 Peak areas are measured by an integrator or other suitable means.
3.6 Interferences (analytical)
3.6.1 Any compound having the general retention time of the analyte or the internal standard used as an interference. Possible interferences should be listed on the sample data sheet. GC parameters should be adjusted if necessary so these interferences will pose no problems.
3.6.2 Retention time data on a single column is not considered proof of chemical identity. Samples over the target concentration should be confirmed by GC/Mass Spec or other suitable means.
3.7 Calculations
3.7.1 The instrument is calibrated with a standard of 0.954 mg/mL butyl carbitol and 0.981 mg/mL butyl carbitol acetate (1 µL/mL) in the desorbing solution. The linearity of the calibration is checked with a standard of 3.82 mg/mL buty]. carbitol and 3.92 mg/mL butyl carbitol acetate (4 µL/mL) in the desorbing solution.
3.7.2 If the calibration is non-linear, two more standards must be analyzed so a calibration curve can be plotted and sample values obtained.
3.7.3 To calculate the concentration of analyte in the air sample the following formulas are used:
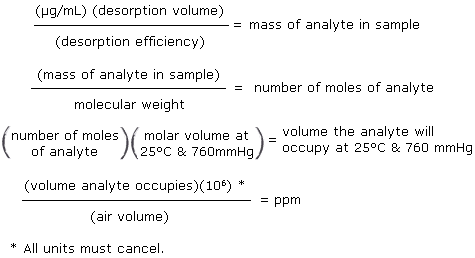
3.7.4. The above equations can be consolidated to form the following formula, used to calculate the ppm of analyte in the sample based on a 10 liter air sample:

µg/mL = concentration of analyte in sample or standard
24.46 = Molar volume (liters/mole) at 25°C and 760 mmHg.
MW = Molecular weight (g/mole)
DV = Desorption volume
10 L = 10 liter air sample
DE = Desorption efficiency3.7.5 This calculation is done for each section of the sampling tube and the results added together.
3.8 Safety precautions
3.8.1 All handling of solvents should be done in a hood.
3.8.2 Avoid skin contact with all solvents.
3.8.3 Wear safety glasses at all times.
4. Recommendations for further study
Collection studies need to be performed.
5. References
5.1. Elskamp, C., Method 83, "2-Butoxyethanol, and 2-butoxyethyl acetate", Organic Methods Evaluation Branch, OSHA Analytical Laboratory, 1990.
5.2. Sax, N., Lewis, R., "Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary", Eleventh Edition, Van Nostrand Reinhold Co., New York, 1987, p. 390.
5.3. Sweet, D., "Registry of Toxic Effects of Chemical Substances", 1985-86 Edition, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, Center for Disease Control, NIOSH, 1987, Vol. 3, p. 2269.